
HTTP/3 is the upcoming version of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which is the underlying protocol used for communication on the World Wide Web. Let us look at some of the most significant changes being made in HTTP/3 and how it proves to be beneficial for both organizations and end-users alike:
QUIC – Secure and reliable connection in a single handshake
QUIC enables secure and reliable connections in a single handshake. This is achieved through a feature called “0-RTT” (Zero Round Trip Time), which allows the client to send data to the server in the first packet itself, without waiting for a response from the server. This reduces the latency and speeds up the connection establishment process. QUIC is that it runs over UDP, which is a connectionless protocol that is less prone to congestion and provides better performance in high-latency networks. QUIC also includes built-in congestion control mechanisms that are designed to prevent network congestion and ensure fair sharing of network resources among different connections.
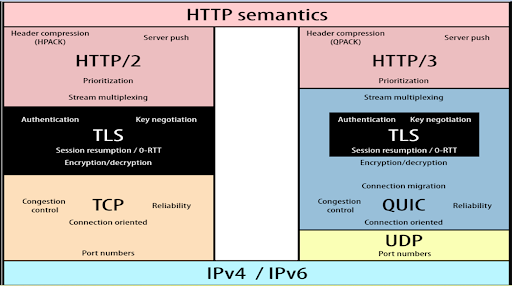
QUIC provides strong encryption by default, using TLS (Transport Layer Security) for secure communication. This helps protect against eavesdropping, tampering, and other security threats. QUIC offers several advantages over traditional transport layer protocols, including improved performance, security, and reliability. It is currently being adopted by major web browsers, servers, and content delivery networks, and is likely to become an essential part of the internet infrastructure in the future.
HTTP/2 vs HTTP/3 RTT
RTT stands for Round-Trip Time, which is the time taken for a request to be sent from the client to the server, and for the server to respond back to the client. Owing to major changes in the way communication occurs in HTTP/3, RTT is expected to be significantly reduced as compared to HTTP/2.
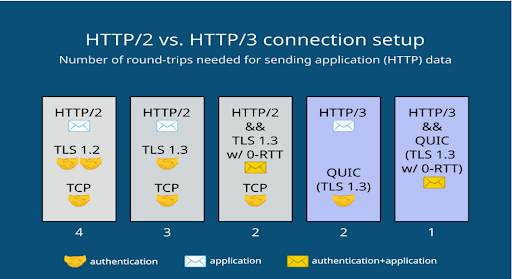
The diagram above compares the connection setup for the HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 stacks:
- The client can send the first HTTP request in the fourth round-trip if HTTP/2 and TLS v1.2 are used.
- With HTTP/2 and TLS v1.3, the first request for application data can be sent in the third or second (on prior connections) round-trip.
- With HTTP/3 and QUIC, which includes TLS v1.3 by default, the first HTTP request is sent in the second or first (on prior connections) round-trip.
In terms of RTT, HTTP/3 has the potential to be faster than HTTP/2 due to the use of QUIC. QUIC’s connection setup process reduces the number of round-trips required to establish a connection, and its congestion control algorithm is designed to reduce latency. However, the actual RTT performance may depend on a number of factors, including network conditions, server, and client configurations, and the specific web application being used.
HTTP/3 QPACK field compression
HTTP/3 uses a new header compression algorithm called QPACK to reduce the amount of data that needs to be transmitted between the client and the server. The QPACK algorithm compresses HTTP headers into a smaller number of bytes before sending them across the network. This helps to improve the performance of HTTP/3 by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted and processed.
Seamless connection migration using Connection ID
HTTP/3 introduces a new feature called “Connection ID” that enables seamless connection migration between network paths or endpoints. The connection ID is a unique identifier assigned to each HTTP/3 connection, and it remains constant even if the underlying network path changes.
Connection ID enables seamless connection migration because it allows clients to move between different network paths or endpoints without interrupting ongoing connections. This is especially important in situations where a client may switch between different types of networks, such as moving from a cellular connection to a Wi-Fi connection, or when a network path becomes congested or unreliable.
Resistance to protocol ossification
HTTP/3 operates in user space rather than the kernel, making new implementations easier to deploy. It has a higher encryption level (e.g., the majority of the QUIC header is encrypted), so middleboxes can’t read the content of the packet and thus don’t drop it — as happens frequently with TCP packets that include a newer feature that middleboxes with older operating systems don’t recognize and consider a security risk.
Support for HTTP/3 in Cavisson NetStorm
Cavisson Systems, Inc is the leading provider of the experience management platform combining performance testing & monitoring, chaos engineering and service virtualization under a single solution to facilitate enterprises in their quest for exceptional customer experience.t.
We have always strived for staying ahead of the curve in terms of adopting and supporting new technologies and we are excited to announce the support of HTTP/3 in our load-testing solution, NetStorm. HTTP/3 is the evolving standard for the next-generation secure and high-performance web applications, and Cavisson System now offers a solution with full testing support for Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) ratification.
Cavisson’s popular load testing solution includes this new functionality, allowing customers to test and validate primary HTTP/3 functionality as well as conduct blended high-scale performance tests across all common HTTP implementations, including HTTP 1.0/1.1 and HTTP/2.
Benefits of HTTP/3 Performance Testing
Scalability testing: Test the scalability of your HTTP/3 applications. You can simulate a large number of users and requests using our proprietary algorithms to see how your application performs under heavy load and identify potential bottlenecks in terms of checking whether HTTP3 requests are processed in a timely and efficient manner.
Performance optimization: Load testing helps in identifying potential performance bottlenecks and allows developers to optimize their code and server configuration accordingly. Optimizing performance on the back of your load test results not only readies your application to handle massive production load but also increases customer satisfaction and retention.
Identifying errors & improving reliability: Cavisson LoadTest can monitor the performance of your HTTP/3 applications in real-time & under load. Identifying errors in your pre-production environment goes a long way in increasing your application’s reliability and ensuring that any unforeseen issues owing to high load are tackled before they affect the end-users.
How to configure HTTP/3 in Cavisson LoadTest?
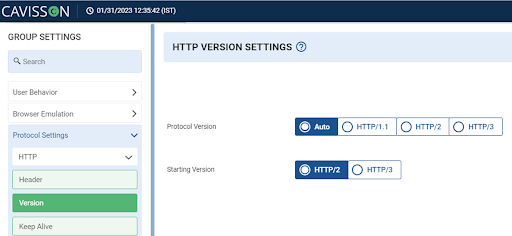
While creating load testing scenarios, you can enable HTTP/3 from Group setting> Protocol setting> HTTP> Version
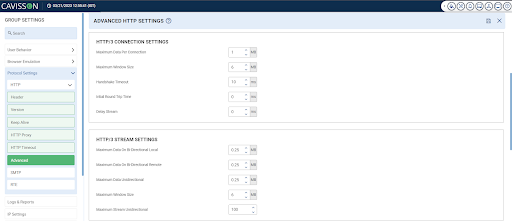
For configuration of HTTP/3 Advanced Setting go to Group setting> Protocol setting> HTTP> Advanced Setting
Perform insightful performance tests & leverage our unparalleled offering to build scalable, resilient and high performing applications on HTTP/3. Coupled with observability and chaos engineering modules, Cavisson’s Experience Management Platform is a one-stop solution to improve customer experience and reduce the mean time to detect & resolve (MTTD & MTTR) issues to stay ahead of your competition.
Click here to learn more about HTTP/3 performance testing with Netstorm.

